Subacute thyroiditis is a relatively rare condition that causes many uncomfortable symptoms for patients. In some cases, the disease can lead to permanent hypothyroidism.
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of the neck that secretes hormones that help regulate metabolism and energy metabolism. In addition, this gland also plays an important role in the body’s physical and emotional responses, such as fear, excitement, and enjoyment.
Thyroiditis (or thyroiditis) includes a group of disorders that cause the thyroid gland to become inflamed. Most cases of thyroiditis lead to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive and produces too much hormone. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland is underactive and does not make enough hormones. Both of these conditions negatively affect a person’s health and well-being.
What is subacute thyroiditis?
Subacute thyroiditis is a rare form of thyroiditis that causes pain and discomfort in the thyroid gland. Patients may also have symptoms of hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism. If left untreated, the disease has the potential to cause permanent complications.
Other names for subacute thyroiditis: de Quervain’s thyroiditis, subacute granulomatous thyroiditis, giant cell thyroiditis.
Causes of subacute thyroiditis
Subacute thyroiditis is thought to be the result of a viral infection. Inflammation usually occurs several weeks after an upper respiratory infection. Mumps virus, influenza virus, and other respiratory viruses can also cause subacute thyroiditis.
The most susceptible population is women between the ages of 40 and 50. However, the disease can appear in both men and women of different ages.
Symptoms of subacute thyroiditis

The most obvious symptom of subacute thyroiditis is pain in the neck caused by a swollen and inflamed thyroid gland. In some cases, the pain can spread to other parts of the neck, ears, or jaw. According to American Thyroid Association, Subacute inflammatory pain usually lasts 1 to 3 months.
Other symptoms of the disease include:
- Soft feeling when gently pressed on the thyroid gland
- Fever
- Tired
- Weak
- Hoarseness
- Difficult or painful swallowing.
Most people develop hyperthyroidism in the early stages of the disease. Symptoms during this stage may include:
- Frequent bowel movements
- Lose weight despite eating normally
- Increased body temperature, sweating a lot
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Weak muscles, shaking hands
- Mood change.
As the disease progresses, the thyroid gland cannot secrete enough of the necessary hormones, leading to later-stage hypothyroidism. Symptoms at this time may include:
- Constipation
- Tired
- Hair loss
- Sudden weight gain
- Dry, pale, cold skin
- Muscle and joint pain
- Slow heart rate
- Mood swings.
Early subacute thyroiditis can last about 2-8 weeks and usually resolves on its own after a few months.
Is subacute thyroiditis dangerous?
According to the Cleveland Clinic (USA), about 5% of patients with de Quervain’s thyroiditis develop permanent complications of hypothyroidism. Cases of disease recurrence are very rare.
Diagnosis of subacute thyroiditis

First, your doctor will perform a physical exam, including an assessment of your thyroid, and ask about your symptoms and medical history. If your doctor suspects you have subacute thyroiditis, your doctor may order some tests to help confirm the diagnosis. These include:
- Thyroid function test: to check the levels of several hormones, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and two thyroid hormones, T3 and T4, in the blood. These hormones vary depending on the stage of the disease.
- Thyroid antibody test
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- C-reactive protein (CRP) test
- Radioactive iodine uptake test
- Thyroid ultrasound.
Treatment of subacute thyroiditis

Your doctor can prescribe medication to help relieve pain and discomfort, and control inflammation. Commonly used medications include:
Anti-inflammatory and pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen help reduce inflammation in the thyroid gland and relieve pain. If these drugs don’t work, your doctor may prescribe prednisone, a corticosteroid, to treat subacute thyroiditis.
Treatment of hyperthyroidism: Beta-blockers help reduce the symptoms of palpitations and tremors in the hyperthyroid phase of the disease.
Treatment of hypothyroidism: Doctors may use levothyroxine to replace thyroid hormone deficiency for patients. This supplement can be short or long term. In the case of permanent complications of hypothyroidism, it is more likely that the patient will need to take medication for the rest of his life.
The use of drugs to treat subacute thyroiditis should follow the instructions and dosage prescribed by a specialist. Patients absolutely do not arbitrarily buy or change the dose without consulting the doctor to avoid side effects or dangerous drug interactions.
Diet for people with subacute thyroiditis
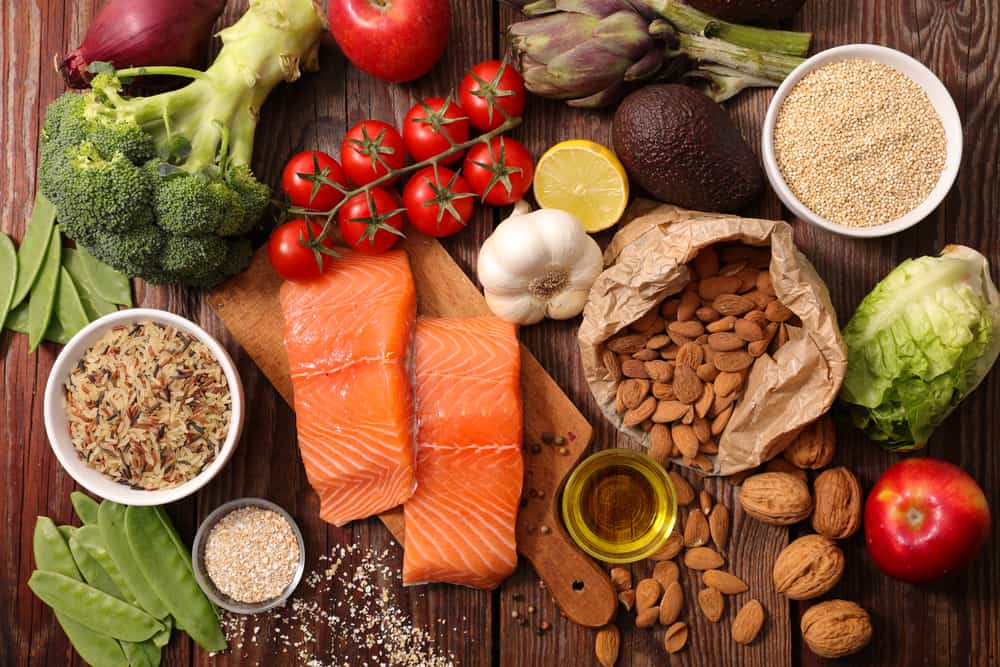

Building a reasonable diet plays an important role in helping patients quickly recover and maintain stable thyroid health. So what to eat with subacute thyroiditis and what to eat?
Experts advise patients to have a balanced diet, full of nutrients, not excessively abstinence. The diet also needs to be suitable for the specific condition and stage of the disease of each person.
Patients should add a variety of green leafy vegetables, fruits, antioxidant-rich foods such as citrus, kiwi, spinach, kale … to strengthen immunity, support thyroid hormone balance . In addition, the patient should also add to the diet nuts (cashew, almonds, walnuts …), fish rich in “good” fats such as salmon, tuna, mackerel … At the same time , it should be noted to increase zinc, calcium and vitamin D to avoid disorders causing mineral deficiency in the body.
Iodine is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones. Therefore, in the period of hypothyroidism, the patient can add foods that provide natural iodine. High doses of iodine supplements from dietary supplements should be consulted with a doctor to avoid counterproductive effects.
Foods that people with subacute thyroiditis should avoid include foods high in sugar, foods containing “bad” fats, animal organs, synthetic sweeteners, alcohol, and stimulants.
Pain from inflammation in the neck or jaw can make it difficult to eat and drink. In this case, it is recommended to prepare soft, easy-to-swallow foods, which can be divided into smaller meals for easier absorption.
Prevention of subacute thyroiditis
Most thyroid diseases do not have a definite way to prevent them. Some other simple methods that can help you strengthen your resistance and prevent infection include:
- Vaccinations such as measles, mumps, rubella, seasonal flu, etc.
- Exercise regularly, fit
- Have a balanced, nutritious diet
- Healthy living habits
- Do not abuse alcohol, beer, stimulants
- Keep nose, throat, chest warm in cold season.
Subacute thyroiditis can be completely cured. Therefore, when you have any unusual symptoms, you should immediately go to reputable medical facilities for examination and advice, to avoid long-term dangerous complications.






